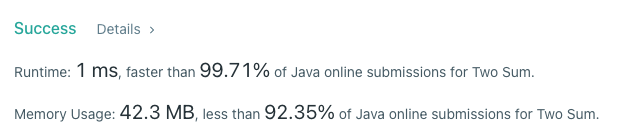
간만에 재미로 다시 푸니까 새롭기도 하고 배우는 것도 있고 좋았다.
일단 테스트케이스
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.assertThat;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
class LC_00001_TwoSumTest {
@Test
void twoSumTest1() {
LC_00001_TwoSum ts = new LC_00001_TwoSum();
int[] result = ts.twoSum(new int[]{2,7,11,15}, 9);
assertThat(result).containsExactly(0,1);
}
@Test
void twoSumTest2() {
LC_00001_TwoSum ts = new LC_00001_TwoSum();
int[] result = ts.twoSum(new int[]{3,2,4}, 6);
assertThat(result).containsExactly(1,2);
}
@Test
void twoSumTest3() {
LC_00001_TwoSum ts = new LC_00001_TwoSum();
int[] result = ts.twoSum(new int[]{3,3}, 6);
assertThat(result).containsExactly(0,1);
}
@Test
void twoSumTest4() {
LC_00001_TwoSum ts = new LC_00001_TwoSum();
int[] result = ts.twoSum(new int[]{0,4,3,0}, 0);
assertThat(result).containsExactly(0,3);
}
@Test
void twoSumTest5() {
LC_00001_TwoSum ts = new LC_00001_TwoSum();
int[] result = ts.twoSum(new int[]{-3,4,3,90}, 0);
assertThat(result).containsExactly(0,2);
}
}
풀이는 퍼포먼스 확인하면서 개선
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class LC_00001_TwoSum {
public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int numI;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
numI = nums[i];
if (map.containsKey(target - numI)) {
return new int[] {map.get(target-numI), i};
}
map.put(numI, i);
}
return null;
}
public int[] twoSum1(int[] nums, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length-1; ++i) {
for (int j = i+1; j < nums.length; ++j) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
return new int[]{i,j};
}
}
}
return null;
}
public int[] twoSum2(int[] nums, int target) {
class Num {
private final int index;
private final int num;
public Num(int index, int num) {
this.index = index;
this.num = num;
}
}
List<Num> numList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
numList.add(new Num(i, nums[i]));
}
Collections.sort(numList, Comparator.comparingInt(v -> v.num));
Num numI;
Num numJ;
int temp;
for (int i = numList.size()-1; i >= 0; --i) {
numI = numList.get(i);
temp = target - numI.num;
for (int j = 0; j < i; ++j) {
numJ = numList.get(j);
if (temp > numJ.num) continue;
if (numJ.num == (target - numI.num)) {
return new int[] {numJ.index, numI.index};
}
}
}
return null;
}
}
2022.04.01 - [Programming] - DI 와 IoC 에 대한 개념과 스프링
DI 와 IoC 에 대한 개념과 스프링
https://github.com/itdar/TIL/blob/main/books/Toby_Spring3.1_vol.1.md 책의 2회독째 3ch 부근에서 확 와닿게 정리되는 문장을 보아서 그냥 줄줄 써본다. 전체 정리를 먼저 해본다면, IoC 는 Inversion of C..
itdar.tistory.com



